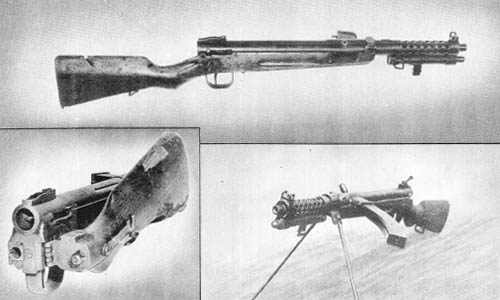
7.92 Submachine Gun: Top. M. P. 43; Center. M. P. 43/1; Bottom, M. P. 44
7.92 Submachine Gun: Top. M. P. 43; Center. M. P. 43/1; Bottom, M. P. 44
The German M. P. 43 is an automatic, air-cooled, gas-operated, magazine-fed shoulder weapon, firing from a closed bolt and a locked breech. Provision is made for both full-automatic and semi-automatic fire. For full-automatic fire, the trigger must be held back until all rounds in the magazine have been fired; for semi-automatic fire, the trigger must be released after each round. However, German official sources say that full automatic fire will be used only in emergency.
Despite the fact that it is of cheap construction, made chiefly of steel stampings, the M. P. 43 is a very serviceable weapon. It is believed that the gun was developed from the 7.92 mm M. Kb. 42 (machine carbine 42) inasmuch as the general design is quite similar, and the same type of ammunition is used. However, the M. P. 43 has a shorter barrel and gas cylinder, and has no bayonet as does the M. Kb. 42.
The receiver, frame, gas cylinder, jacket, and front sight hood are made from steel stampings. As all pins in the trigger mechanism are riveted in, it cannot be disassembled, although a complete trigger assembly may be very quickly inserted. The gas piston assembly, bolt, hammer, barrel and gas cylinder are machined parts.
The gas piston assembly consists of a piston, piston rod, and slide which appear to be machined from one piece with a stamped handle inserted. The stock and pistol grips are of low grade wood. The curved magazine is inserted from the bottom, and the fired cartridge cases are ejected on the right.
The various models of this weapon, including the M. P. 43, M. P. 43/1, and M. P. 44, have been officially designated M. P. 44. A recent official German order changed the nomenclature to Sturmgewehr 44.
SPECIFICATIONS
| Caliber |
|
7.92 mm (.312 in.) |
| Weight (with empty magazine) |
|
10 lb., 1 oz. |
| Length (overall) |
|
3 ft., 1 in. |
| Length of barrel |
|
16.2 ins. |
| Sight radius |
| Principle of operation |
|
gas |
| Feeding device |
|
Curved magazine |
| Capacity of feeding device |
|
30 rounds |
| Cooling system |
|
air |
| Ammunition types |
|
7.92 mm Postolen Patronen |
|
|
Semi AP., M.P. 43 |
| Effective rate of fire |
| (automatic) |
|
100 to 120 rds./min. |
| (semi-automatic) |
|
40 to 50 rds./min. |
| Type of sight |
|
Leaf sight graduated from 100 to 800 meters |
| Rifling |
| Twist |
|
R.H. |
| No. of grooves |
| Chamber pressure |
| Muzzle velocity (approx.) |
|
2250 f/s |
| Muzzle energy |
| Maximum range |
| Effective range |
|
400 yds. |
German: p. 206.1 (March 1, 1945)